Why have so many Californian's moved to Texas?
Since the 2020 US Election, California has seen an acceleration of families leaving the state. Cost of living, crime, lack of job opportunities and lack of governance all cited from Californian's of all ages and income groups.
San Francisco 1906, the City by the Bay was hit by an earthquake measuring 7.9 on the Richter scale. Deaths from the earthquake were estimated between 700-3,000. 225,000 people were left homeless, over half of the city’s population.

While the earthquake was devastating, 90% of the damage was caused by fires from ruptured gas mains. Many insurers refused to cover properties for earthquake damages.
So homeowners set fire to their homes to collect insurance, further increasing the chaos. Damages rose to the equivalent of $11,400 million.
The Great Californian Exodus
Fast forward 115 years, another exodus from the west coast is occurring. Gary Buechler, a father of two and lifetime Californian recorded an informative short video commentary.
Gary owned a thriving comic book shop for 10 years in downtown San Francisco, his wife, ran Secret Agent Salon in Pacific Heights. A successful hair-dressing salon with many A-listers on the books. Both were forced to close their businesses.
Here are the medium to long term structural problems from California face.
Cost of Living
2021 US Income Tax Rates
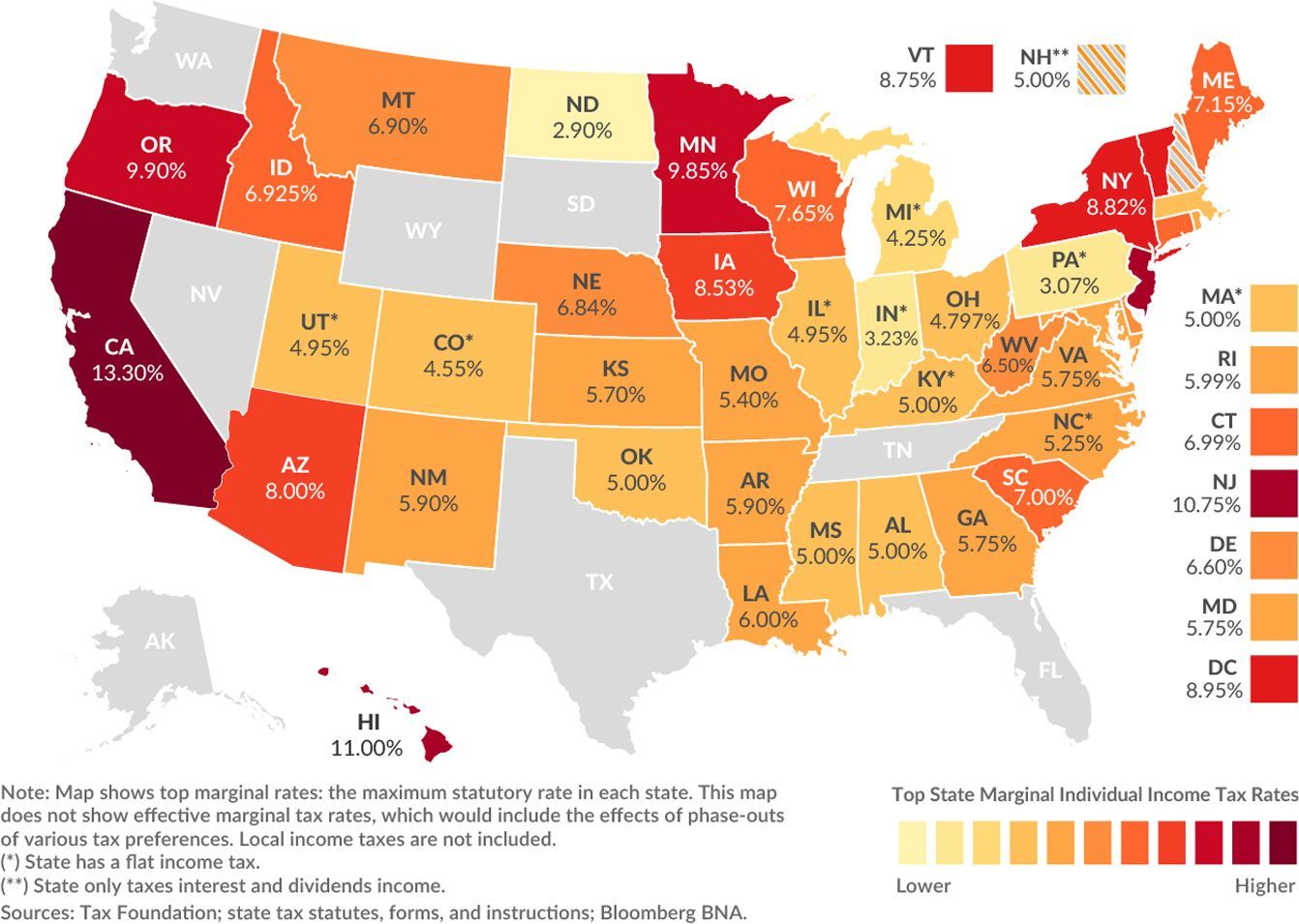
California Legislative Analyst’s office reports about a million people left the state between 2007 and 2016. With the highest income tax rates (13.3%) in the country, Neighbouring states Nevada and Texas, do not levy any state income taxes.
Job Opportunities
During 2009-16 over 13,000 Californian business left the State. This year, Charles Schwab, Hewlett-Packard, Occidental Petroleum and Tesla announced they would leave San Francisco, many heading to Texas.
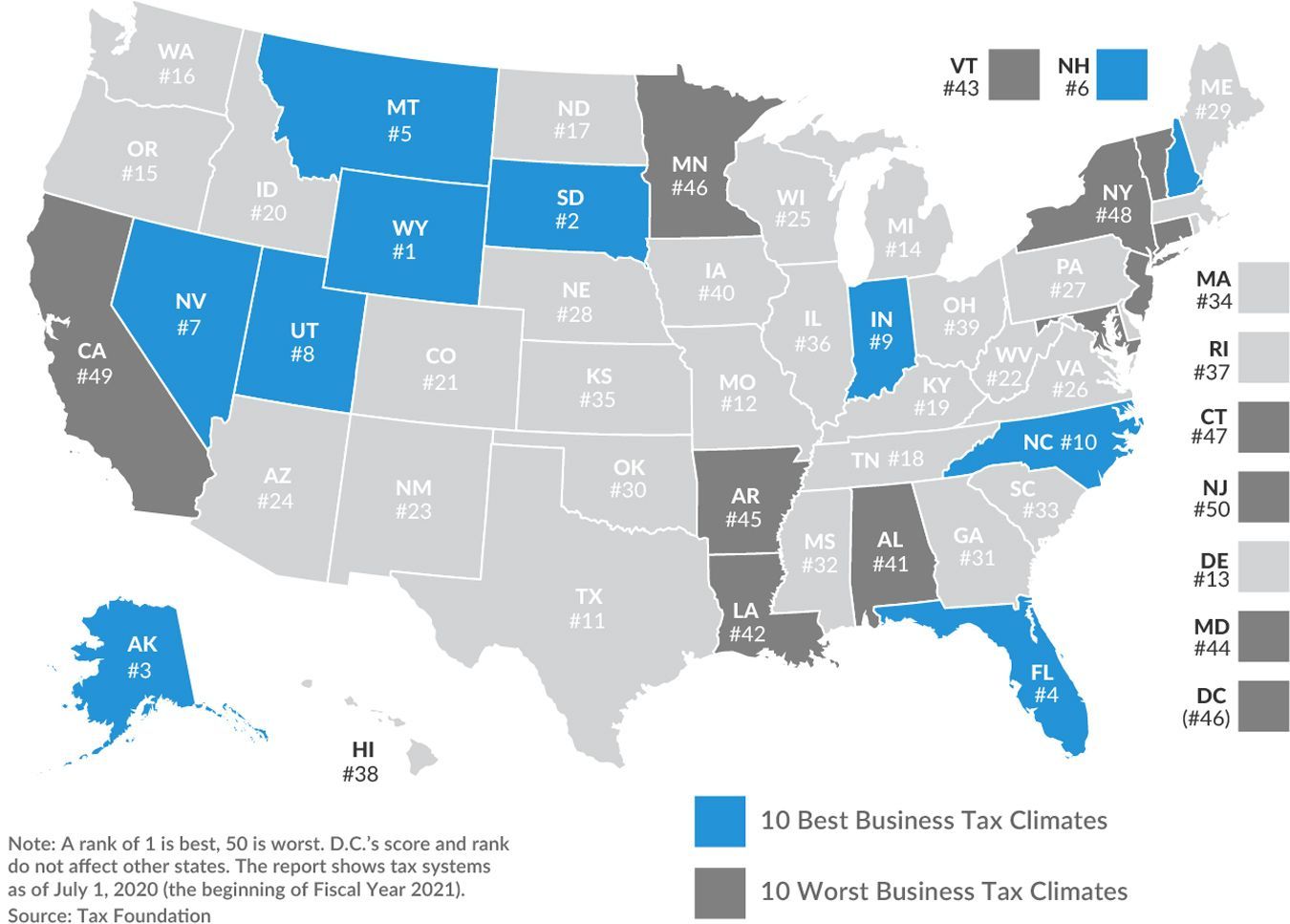
California, New York and State of New Jersey now have the three worst business tax climates in the country. Texas is a healthy 11th and Florida also very commerce friendly.
Gas Prices at the Pump
Californians have seen prices at the pump rise 33% in the last year. The average price as of April 2021 is around $4 per gallon. Whilst Texans have seen a 45% increase, their highs are still under California's 12 month low of $2.70 per gallon.
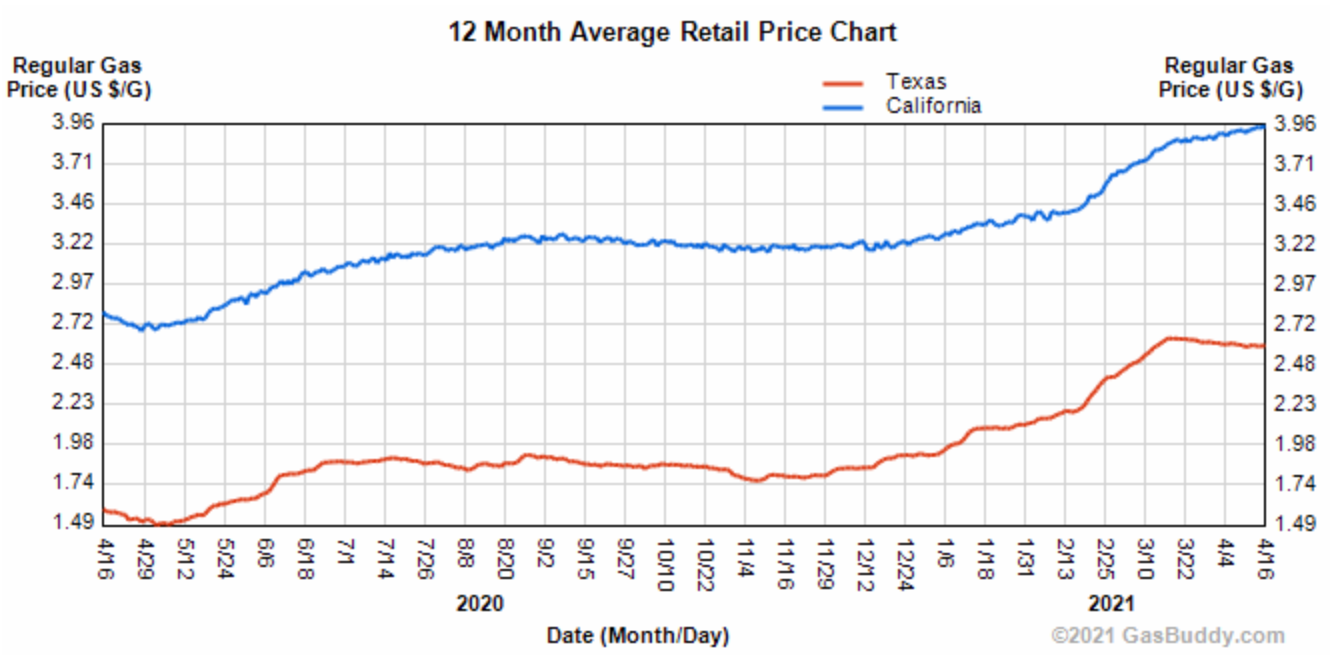
Texan gas prices at the pump are currently averaging 35% cheaper per gallon – $2.60 per gallon in contrast to California's $4 per gallon.
California's politicians have been consistent and strong advocates for "green renewables". Pushing ahead with laws to help advance new solar and wind entrants into the energy market.
To pay for this technology, traditional energy providers have had to pay tax credits to help subsidise their entry into the market.
Electricity Prices
Residential electricity bills have ballooned in Democratic States. State subsidies needed to finance new solar developments and battery storage for additional grid capacity have been passed onto households.
| Rank | US State | Average Electricity Price per kWh |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Hawaii (D) | 29.14 |
| 2 | Rhode Island (D) | 22.59 |
| 3 | Alaska (D) | 21.93 |
| 4 | Massachusetts (D) | 21.54 |
| 5 | California (D) | 20.45 |
| 6 | Connecticut (D) | 20.39 |
| 7 | Vermont (D) | 19.04 |
| 8 | New Hampshire (D) | 18.74 |
| 9 | New York (D) | 18.23 |
| 10 | Maine (D) | 16.51 |
| 25 | Texas (R) | 11.87 |
| 26 | Florida (R) | 11.86 |
Source: State Rankings: US Energy Information Administration Dec 2020
Why are Californian Electricity Prices so Expensive?
California's Renewables Portfolio Standard (RPS) program was established in 2002 which required 20% of all the State's electricity be served from renewable resources by 2017.
The costs to transition has been immense on the poor, the working and middle classes. 9 million Californian's (of a population around 40 million) were unable to pay their energy bills in 2020.
The Californian Public Utilities Commission reported electric and gas utility customers had accumulated $1,150 million in unpaid bills. Regardless, California will require utilities to use 100% green renewables by 2045.
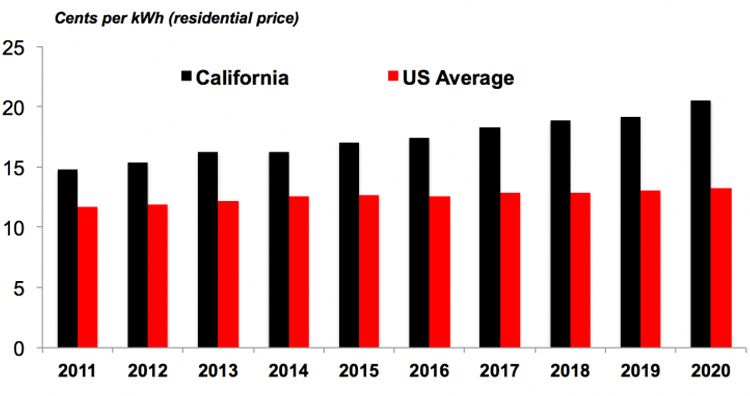
• Pacific Gas and Electric’s rates are 80% above the US average.
• Residential prices in San Diego Gas & Electric are double the US average.
• Southern California Edison’s prices is now 45% higher than the US average since 2013.
Californian Paying for Solar Incentives
The California Solar Initiative Program which ended 2016 provided incentives for both residential and non-residential photo-voltaic systems. These employ solar modules, each comprising of solar cells, which generate electrical power.
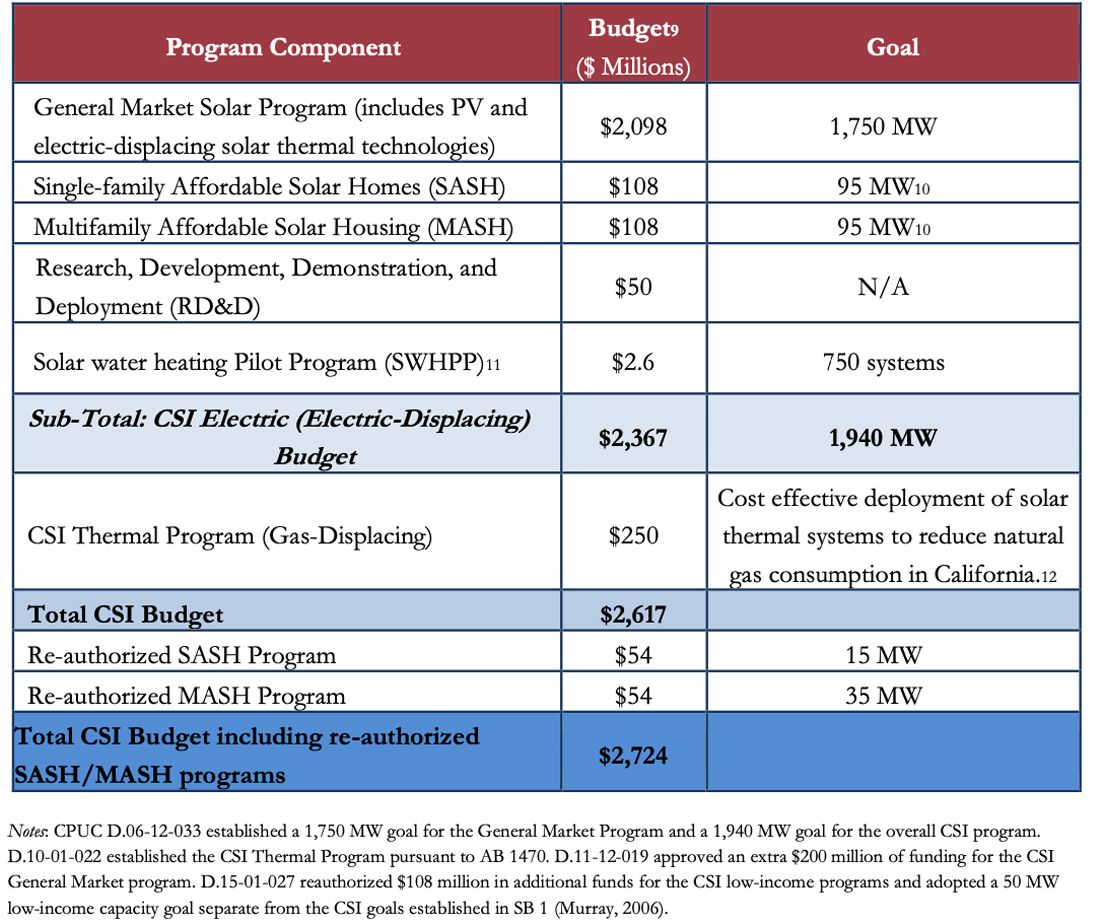
The CSI program has two funding streams, depending on whether the incentivised solar technology is used for electricity generation or displacing natural gas consumption. The electric portion of the CSI program has a 10-year budget of $2,724 million.
All collected from the Californian electric ratepayer.
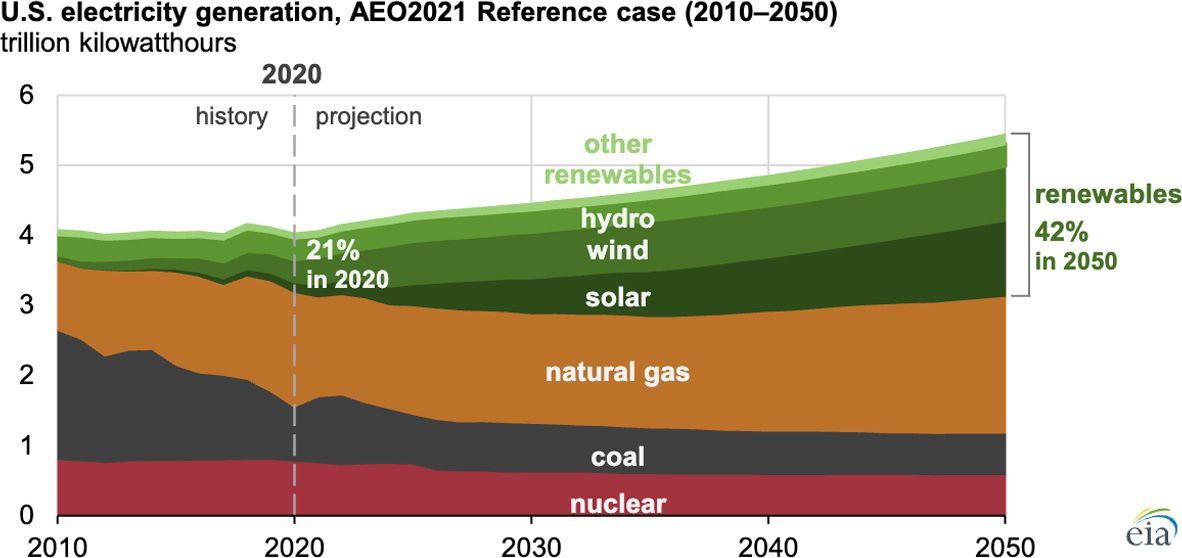
Worryingly, the EIA projects renewables will account for 42% of all US electricity generation by 2050. A doubling from 2021.
The subsidies given to solar and wind companies to penetrate the energy market has come through increasing the cost to oil and gas producers - an energy tax which is then passed onto residential consumers.
The net result, along with the unease with the implications of the US election results, in a state that has been heavily blue for years (Senator Pelosi, Governor Newsome, Mayor London of San Francisco) have propelled many in their decision to Calexit.
When in Texas
The realisation that zero state income tax, 35% cheaper gas prices, 50% cheaper electricity prices. But new Texan's should be aware.
The increase of intermittent wind turbine energy infrastructure currently being added into the Lone Star State's energy mix.
Mandated by the previous Obama administration, if not corrected, will provide more unreliable and highly unstable energy supply to the grid.


